This is the first monthly posting in what we intend to become a regular series of patent highlights, a showcase of the intellectual property we have been reviewing during the past month. We hope that it will be useful to the public.
PLEASE CITE AS: Mucke HAM. Patent Highlights for December 2010. Published online in the H.M. Pharma Consultancy Blog (http://hmpharmacon.blogspot.com) on January 3, 2011. Archived at
PLEASE NOTE: Depending on how quickly ESP@CENET integrates the newest PCT documents, hyperlinks to the most recently published patents might not yet be active when this post goes online. This should remedy itself within a few days.
Two New Uses For Opioid Receptor Antagonists: Cancer Therapy Fatigue And Paraphilia
If you have thought that all conceivable uses for opiate receptor antagonists have already been claimed, here are two new ones for you: the Massachusetts General Hospital got WO2010/141666 published on Dec. 9, 2010. It claims that fatigue-causing increases in systemic beta-endorphin levels which are caused by extensive exposure to outdoor cutaneous UV irradiation, ionizing radiation or administration of chemotherapy can be modulated with opiate receptor antagonists, e.g. naloxone. WO2010/142696 (Humboldt University Berlin-Charite [DE], Dec. 16, 2010) claims naloxone or naltrexone for the treatment of sexual paraphilisms – a term which describes “recurrent, intense sexual urges, fantasies, or behaviours that involve unusual objects, activities, or situations and cause clinically significant distress or impairment.”
A “Kiss” For Schizophrenia
Kisspeptins (initially called metastins, because they suppress metastases) are neuropeptides encoded by KISS1 and bind to a receptor that was originally known as GPR54, AXOR12 or hOT7T175. They act as gatekeepers of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. The literature on this subject focuses on reproductive development and fertility; eg., Front Horm Res . 2010; 39: 25-36 ). The commercial arm of the Weizmann Institute now claims kisspeptin receptor ligands to treat abnormalities in sensory gating function, as they typically occur in schizophrenia ( WO 2010/137022 , Yeda R&D Co. Ltd. [IL], Dec. 2, 2010). The companion peer-review paper is Mol Psychiatry 2010; 15(4): 415-25 .
Ligands For Less-Conventional Drug Targets, TAAR, NAMPRT, TRPM, And AhR
-
WO2010/139707 (Roche Ltd [CH], Dec. 9, 2010) — The 2-aminooxazolines presented here are ligands at the trace amine associated receptor 1 (TAAR1; see review in JNeurochem. 2011; 116(2):164-76 – PDF ), and therefore suitable for the treatment of neuropsychiatric and metabolic disorders, disorders of sleep and circadian rhythm, and cardiovascular disorders. Roche‘sApril15, 2010developmentpipelinesummary states that the company has a TAAR1 partial agonist, RG7351, in clinical Phase I for depression.
-
WO 2010/142735 (TopoTarget A/S [DK], Dec. 16, 2010) — The pyridinyl compounds presented are said to treat elevated levels of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPRT), as seen in diabetic nephropathy, rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, and COPD.
-
WO 2010/144679 (Janssen Pharmaceutica NV [BE], Dec. 16, 2010) — Benzimidazoles for the treatment of disorders and conditions modulated by the TRPM8 (transient receptor potential melastatin subfamily type 8) channel, such as inflammatory and neuropathic pain, and cardiovascular or pulmonary diseases aggravated by cold. The company hasn’t announced a lead with this action yet.
-
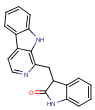
WO2010/148350 (Cornell University [US], Dec. 23, 2010) — Simply exposing an aqueous solution of tryptophan to window sunlight for one week results in multiple photoproducts that activate the arylhydrocarbonreceptor (AhR, a cytosolic transcription factor that becomes active only after ligand binding), and increase the production of AhR target genes and proteins in hepatocytes. Three photoproducts were characterized, and shown to have biologic activities. One of these, 3-{9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-1-ylmethyl}-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-one, is stated to be a new chemical entity (see image). We can confirm that no compounds with 95% or higher chemical similarity ratings are listed in PubChem.
Tellurium-Containing And Insecticide Antivirals
-
In WO2010/146585 (Biomas Ltd. [IL], Dec. 23, 2010) we find claims for anti-influenza drugs which are removed from the medicinal chemistry mainstream – they contain tellurium. This is unusual but not unheard of: Te-containing scaffolds with antiviral and/or immunomodulatory action have been described, including ammonium trichloro(dioxyethylene-O,O’)tellurate (Biomas’ AS101; BrJDermatol. 2009; 160(2): 403-8) and [TeO4(COCH)2]2 (SAS) which feature prominently in this invention. Other antioxidant and neuroprotective oragnotellurium compounds, such as diethyl-2-phenyl-2-tellurophenyl vinylphosphonate (DPTVP), are also known from the peer-review the literature ( ToxicolSci. 2010; 115(1): 194-201 ). Selenium-containing compounds with pharmacological activity have been investigated much more frequently, most famously perhaps ebselen (2-phenyl-1, 2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one; see e.g., ExpertOpinInvestigDrugs 2000; 9(3): 607-19 ).
-
Spinosyns, a class of glycosylated macrolactones from the soil bacterium Saccharopolyspora spinosa , were originally discovered at Eli Lilly in the course of a drug screening program. Spinosad (85% spinosyn A, 15% spinosyn D) has been developed by Dow AgroSciences LLC as an insecticide and ectoparasite treatment ( CurrTopMedChem 2002; 2(7): 675-99 ). A Greek company has now found ( WO2010/150100 by Entarco SA [GR], Dec. 29, 2010) that spinosad can be used to treat herpes simplex and influenza virus infections, and is an antiprotozoal and anticancer agent as well; apparently because spinosyns block mitochondrial respiration. The action against Plasmodium species, which produce ATP exclusively through the glycolytic pathway but need oxidative phosphorylation for pyrimidine biosynthesis, could also be explained on this basis. Other uses for spinosyns have been reported by Eli Lilly, e.g. in US2007/0167379 where they are claimed as promoters of wound healing.
In Vitro Assessment Of Respiratory Toxicity
WO 2010/141954 (CeeTox, Inc. [US], Dec. 9, 2010) — Respiratory toxicity of compounds is assessed by measuring the expression of markers such as CYP1A1, Bcl-2, IL-6, IL-8, CD-86, glutathione, and lactate dehydrogenase using MatTek Corp.’s human 3-D EpiAirway ™ organotypic tissue culture model and applying multiple-endpoint analysis. An indication of organ specificity is provided by a toxicity index, which compares mean IC50 values in lung cells to mean IC50 values in liver cells. CeeTox has presented a poster on this subject at the 2009 World Congresses on Alternatives & Animal Use in the Life Sciences, held a few weeks after the U.S. priority date of this application.
Microacoustic Biosensors For Direct Pathogen Detection
Piezoelectric biosensor chips for rapid infectious disease diagnostics are described in WO2010/138871 (Aviana Molecular Technologies, LLC [US], Dec. 2, 2010). Usually such systems are configured to detect antibodies, but here the principle is turned on its head: Microfluidic channels, coated with single crystal substrates which in turn carry pathogen-specific binding films, are exposed to the analyte. Ultrasound is applied, and the propagation of waves in what is called layerguidedshearhorizontalacousticplatemode is monitored to detect mass changes effected by the binding of pathogens such as Dengue virus, Chlamydia trachomatis , or Neisseria gonorrhoeae . The biosensors, which can be multiplexed to provide simultaneous detection of multiple pathogens, allow for portable real-time point of care analytical systems in cost sensitive and/or resource limited settings.
Saliva Biomarkers For Pancreatic Cancer
WO2010/151789 (University of California [US], Dec. 29, 2010) — Pancreatic cancer still has a dismal prognosis (in the U.S., it is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths, despite its relatively low incidence), mainly because its typical symptoms tend to manifest only in late-stage disease. Raising the diagnostic red flag early, using non-invasively obtained body fluids, could save more lives than conceivable advances in chemotherapy. A logistic regression model based on a combination of four mRNA biomarkers ( KRAS , MBD3L2 , ACRV1 , and CDKL3 ) provided the highest discriminatory power for differentiating pancreatic cancer subjects from non-cancer subjects ( ROC – plot area under the curve (AUC) value of 0.971, 90.0% sensitivity, 95.0% specificity using a cutoff of 0.433). The triplet of KRAS, MBD3L2, and CDKL3 distinguishes pancreatic cancer from chronic pancreatitis (AUC = 0.981; 96.7% sensitivity; 96.7% specificity). Also of note is the discriminatory power of a combination of two bacterial biomarkers ( N. elongata and S. mitis ) (AUC = 0.895; 96.4% sensitivity; 82.1% specificity).
A New Facet On Proteomics Technology
WO 2010/140774 (Korea Basic Science Institute [KR], Dec. 9, 2010)
This is a mass spectroscopy method for analyzing proteins. Retention time and mass value of the peptide are determined through data-independent analysis, and sequential database lookup operations to identify proteins are performed in primary protein sequence databases using the ProteinLynx Global Server™ (PLGS; Waters) and MASCOT search engines. Results are compared to verify the qualitative and quantitative analysis on the protein.